Why Website Speed Matters
We live in a fast-paced digital world where Social Media got us used to thousands of new content in a flick of a finger. And we know it's not fair, but users are expecting exactly the same from your website. So loading speed is incredibly important, especially when regarding mobile users or online shoppers.
Here are some facts
According to Google, as page load time increases from one to ten seconds, the probability of visitors leaving your website increases by 123%.
53% of mobile site visitors will leave a page that takes longer than three seconds to load.
Amazon saw a 1% revenue increase for every 100 milliseconds of improvement in page load time. 1% does not seem a lot, but believe us, for Amazon it is.
So, what's the impact on a website?
- User Experience and Satisfaction
When it comes to user experience, speed is paramount. Visitors expect websites to load in the blink of an eye. Slow-loading pages frustrate users and often lead to high bounce rates. - First Impressions
Your website's speed is often the first impression users have of your brand. A sluggish website can deter potential customers before they even explore your content. - Mobile Friendliness
As mobile devices dominate the internet landscape, a fast-loading website is essential for catering to mobile users. Google's mobile-first indexing prioritises fast websites in search results. - Conversion Rates
Speed influences your website's ability to convert visitors into customers. A faster site tends to have higher conversion rates, boosting your bottom line. - Improved Search Ranking
Search engines, particularly Google, consider page speed as a ranking factor. Faster websites tend to rank higher in search results, as they allow engine bots to crawl content more efficiently.
Quick Tips to Boost Website Speed
- Optimise Images
Compress and resize images to reduce load times. It seems obvious, but we are often surprised by how many high-resolution images are still being used on websites. - Minimise HTTP Requests
Reduce the number of requests by using fewer resources on your page. These can be external scripts, User Interface libraries or content sources. Load assets as and when users require them instead of all upfront. - Leverage Browser Caching
Set up browser caching to store frequently accessed resources on users' devices. - Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Use a CDN to distribute your content across multiple servers for faster delivery. - Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources
Identify and minimise render-blocking CSS and JavaScript files. - Regular Performance Testing
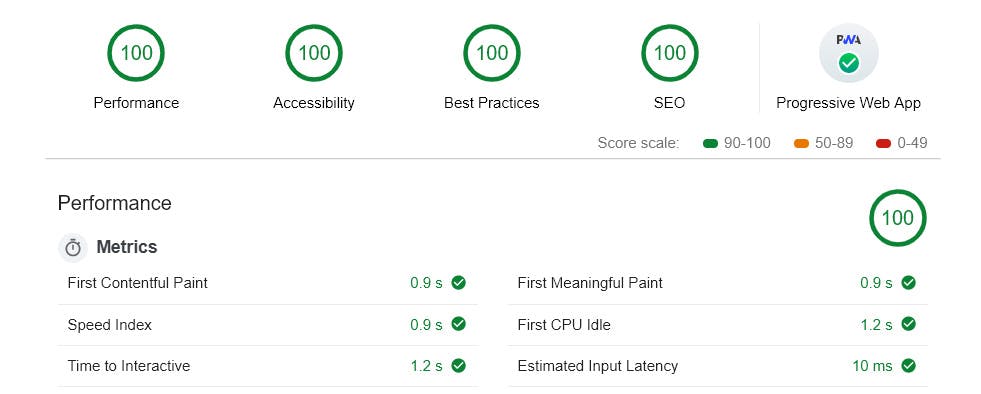
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to regularly check your website's performance. All Core Web Vitals should ideally be above 90 which is not always easy and may take time and effort.